
newYou can listen to Fox’s news articles!
Pain medications used for lower back pain can be associated with high risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI). New research.
The study is published online in the Journal Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine, and found that some groups previously thought to be too young to develop a condition that was more than twice as risky when gabapentin was taken.
“Our findings show the association between prescriptions of gabapentin and dementia or cognitive impairment within 10 years,” the researchers said in a press release.
Survivors of breast cancer may be at a lower risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease, researchers say
The drug is becoming increasingly popular for treating chronic pain, especially neuropathic pain, the researchers noted in a press release.
Gabapentin, which is also used to control seizures, has relatively low addictive potential compared to Traditional opioids.
Gabapentin is becoming increasingly popular for treating chronic pain, especially neuropathic pain (neuronal) pain, experts say. (istock)
Recent research has raised new concerns about its side effects, including potential association with neurodegeneration.
Previous findings could not confirm specific links. Specific age groups It’s more vulnerable.
In the most recent study, researchers collected data from Trinetx, a health research network that includes electronic health records from 68 healthcare institutions across the United States.
Despite health risks, more seniors are using cannabis more than ever before;
Looking at anonymous records of adult patients, the team looked at groups prescribed gabapentin for chronic sub-ranking Back pain Between 2004 and 2024, we compared them with people who were not receiving the medication. There was a total of 26,414 individuals in each group.
The researchers described factors such as demographics, coexistence conditions, and the use of other pain-relieving medications.
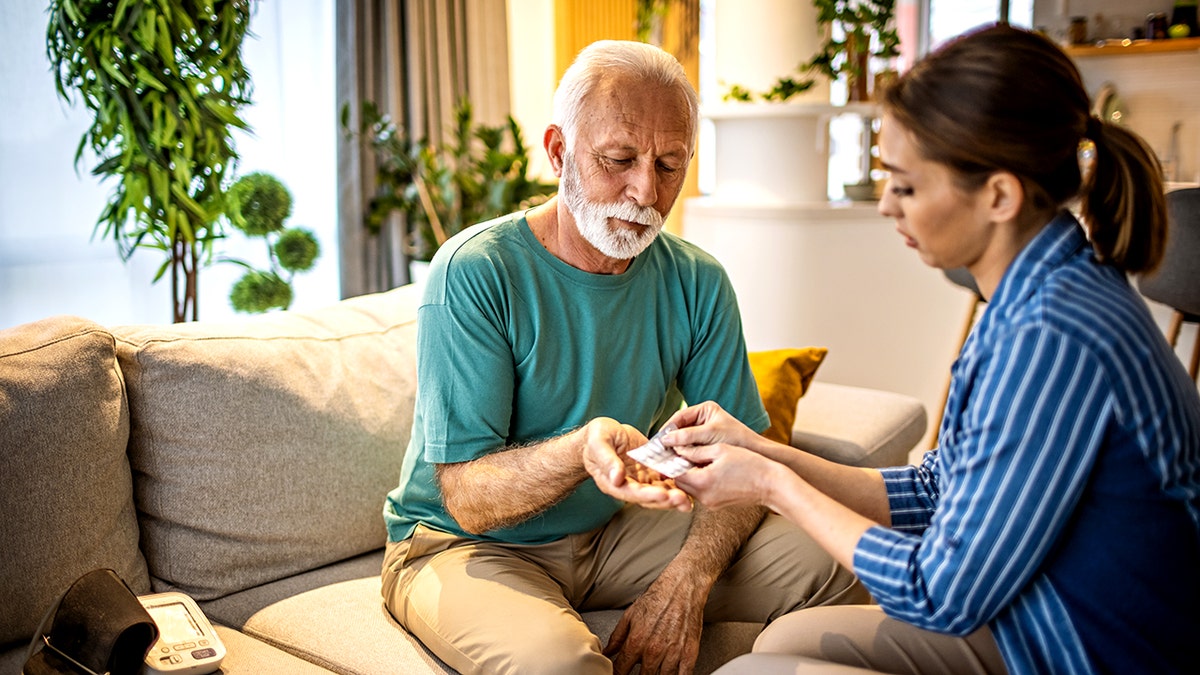

People ages 18-64 who received gabapentin were more than twice as likely to develop conditions than those who were not prescribed the medication. (istock)
Patients who received gabapentin prescription were 29% more likely to be diagnosed With dementia And there is an 85% higher chance of being diagnosed with MCI within 10 years of initial pain diagnosis, the study found.
Click here to get the Fox News app
Looking at certain age groups, people ages 18-64 who received the medication could develop more than twice as much condition as those who were not prescribed gabapentin.
Click here to sign up for our health newsletter
There was no increased risk among people aged 18 to 34. I prescribed medicationthe risk of dementia was more than twice as high (and three times more) increased between the ages of 35 and 49.
Researchers observed a similar pattern between the ages of 50 and 64.
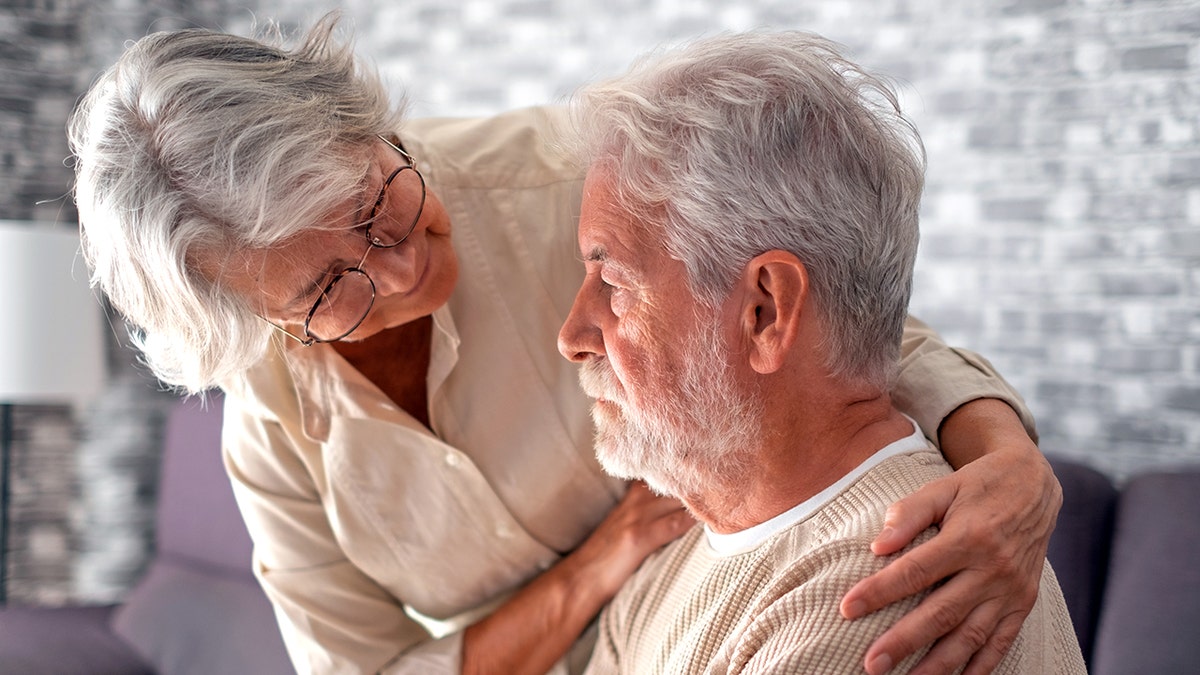

The study found that more than six or more patients who received a prescription for gabapentin were 29% more likely to be diagnosed with dementia and 85% more likely to be diagnosed with MCI within 10 years of their initial pain diagnosis. (istock)
The frequency of prescription increased the risk. Patients with 12 or more prescriptions were 40% more likely to develop dementia than patients who were prescribed gabapentin 3-11 times, and 65% were 65% more likely to develop MCI.
“Our findings show a link between prescriptions of gabapentin and dementia or cognitive impairment within 10 years.”
This study had several limitations. As this was an observational study, it was not possible to draw solid conclusions about causes and effects, the researchers noted.
Visit us for more health articles www.foxnews.com/health
They also acknowledged that the study was retrospective and could not explain the dose or length of gabapentin use.
The results “support the need for close monitoring in adult patients who have prescribed gabapentin to assess potential cognitive decline,” the researchers added.






