
newYou can now listen to Fox News articles.
Chronic kidney disease is listed as the 9th leading cause of death worldwide.
A record number of men and women are now estimated to have compromised kidney function, according to a new study following one published in The Lancet.
Researchers from New York University Langone Health, the University of Glasgow, and the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington analyzed the rise in infections. kidney disease all over the world.
Quitting alcohol and medication sooner could prevent ‘silent killer’, experts say
They examined 2,230 published papers and health datasets from 133 countries, examining diagnoses, mortality, and health outcomes. compensation for disability From illness.
From 1990 to 2023, the number of infected people increased from 378 million to 788 million, making it among the top 10 deadliest diseases in the world for the first time.

The biggest risk factors for kidney disease include high blood sugar, high blood pressure, and high body mass index (BMI). (St. Petersburg)
The study was conducted as part of the 2023 Global Burden of Disease Study, which also found that approximately 14% of the world’s adult population is ill. chronic kidney disease. Approximately 1.5 million people will die from kidney disease in 2023, an increase of more than 6% compared to 1993.
Most people in the study were in the early stages of the disease, which can be improved with medicines and drugs. Lifestyle changes Researchers noted that caution should be taken before dialysis or surgery becomes necessary.
The study, presented last week at the American Society of Nephrology’s annual Kidney Week meeting, is “the most comprehensive estimate of the condition in nearly a decade,” the authors said.
Diabetes research reveals diagnostic gap affecting millions
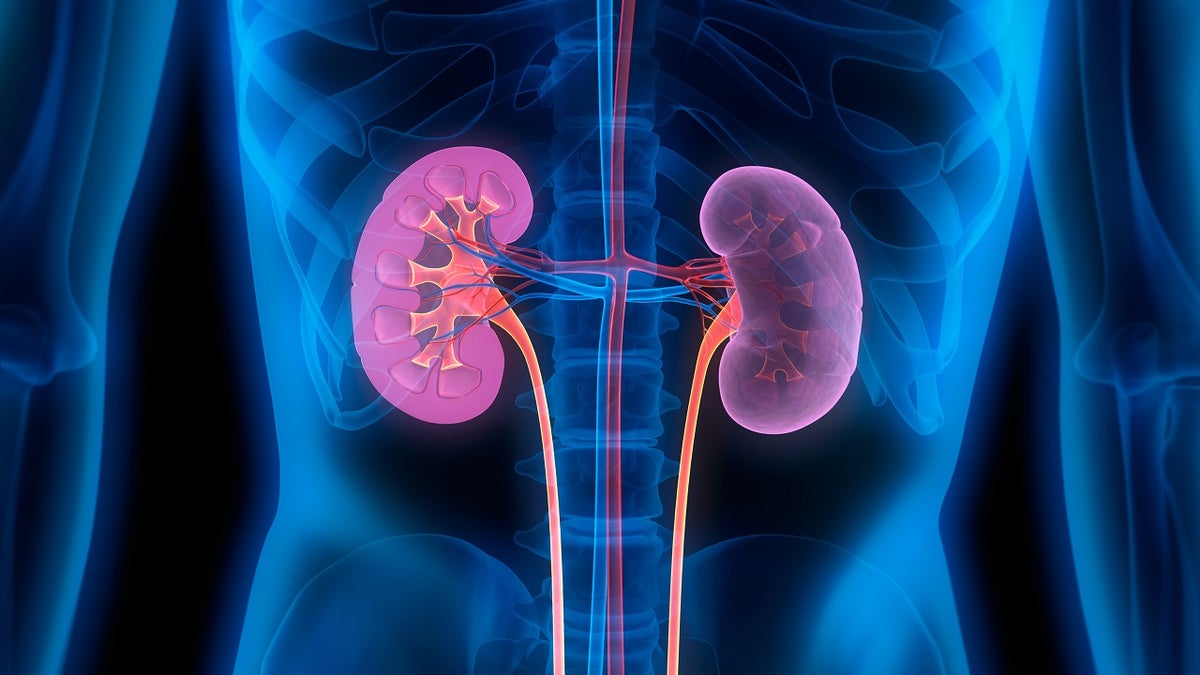
With chronic kidney disease, the kidneys lose their ability to filter waste and excess water from the blood, explains New York University Langone.
Mild cases may have no symptoms, but the most advanced stages may require dialysis, kidney replacement therapy, or treatment. organ transplant.

Chronic kidney disease causes the kidneys to lose their ability to filter waste and excess fluid from the blood. (St. Petersburg)
Kidney dysfunction has also been identified as a major risk factor for heart disease, contributing to approximately 12% of global cardiovascular mortality.
Research shows that the biggest risk factors for kidney disease include high blood sugar; high blood pressure and high body mass index (BMI).
Click here to download the FOX News app
Joseph Koresh, MD, co-author of the study and director of the New York University Langone Institute for Optimal Aging, said these results classify chronic kidney disease as “common, deadly, and a worsening public health problem.”
“These findings support efforts to recognize the condition alongside cancer. heart disease And mental health concerns are a key priority for policymakers around the world,” he said in a statement.

Kidney disease may have no symptoms, but may eventually require dialysis or an organ transplant. (St. Petersburg)
Study co-lead author Morgan Graham, MD, Susan and Morris Mark Professor of Medicine at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine, also commented that chronic kidney disease is “underdiagnosed and undertreated.”
“Our report highlights the need for increased urine testing for early detection and for patients to be able to afford treatment once diagnosed,” she wrote.
Click here to sign up for our health newsletter
Recently, new drugs have become available that can slow the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of the disease. heart attack, stroke Graham added that it may take time to see the global impact, but heart failure.
He called for doctors to be more aware of kidney function and the effects of certain medications. (St. Petersburg)
Fox News senior medical analyst Dr. Mark Siegel commented on the “dramatic increase” in an interview with Fox News Digital, agreeing that kidney disease is “significantly underdiagnosed and vastly underdiagnosed,” in part because there are no symptoms in its early stages.
“The kidneys are waste filters and are responsible for managing electrolyte and acid/base balance,” said Professor Siegel, who was not involved in the study. “They are very sensitive to changes in blood pressure and blood flow, and damage can lead to loss of proteins and electrolytes.”
Test yourself with our latest lifestyle quiz
He added: “Hypertension, obesity, heart disease, diabetes and low blood pressure all affect basic kidney function, making secondary kidney disease and failure more likely in addition to primary damage to the kidney itself.”
For more health stories, click here
Dr. Siegel urged physicians to be more aware of kidney function and its effects. certain medicines.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Gates Foundation, and the National Kidney Foundation.






